What is BASE, Coinbase Layer 2 Network?

TL;DR
Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 solution developed by cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase, in partnership with Optimism to provide a secure, cost-effective and developer-friendly environment to build on-chain applications.
Base is compatible with all EVM-wallets and the Coinbase wallet.
Base has diverse use cases including payment apps, token swaps, liquidity provision, token bridging and launching DAOs.
What Is Base?
Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) blockchain officially released on August 9, 2023 by US-headquartered crypto exchange Coinbase. Base garnered attention in the crypto community because it’s the first blockchain launched by a publicly traded company.
Base was developed in partnership with Ethereum L2 blockchain Optimism on the OP Stack, a standardized and open-source development stack that powers Optimism. Base allows developers to build decentralized apps (DApps) with access to Coinbase’s ecosystem of 110 million verified users and more than $80 billion assets.
Base’s vision is to create a so-called Superchain powered by Optimism supported by a community of developers. Base has publicly announced that it doesn’t currently plan to issue a new network token for Base, therefore users should be extremely cautious about scammers that offer fake Base tokens.
What is Layer 2?
Layer 2 blockchain is a term used to describe secondary protocols or frameworks built on top of an existing blockchain network (Layer 1) such as Ethereum. The primary purpose of Layer 2 solutions is to improve the scalability, transaction throughput, and efficiency of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain, without compromising its security or decentralization.
There are several types of Layer 2 blockchain technologies, including state channels (Lightning network for Bitcoin and Raiden network for Ethereum), sidechains (Liquid network for Bitcoin and Loom network for Ethereum), and rollups (Optimistic rollups and ZK-rollups).
Some of the most widely used Layer 2 blockchain networks include Optimism, Polygon, zkSync, and Arbitrum.
What is Optimism?
Optimism is a Layer 2 blockchain solution built on top of the Ethereum network, aiming to improve its scalability, transaction throughput, and reduce associated fees. Optimism leverages a technology called Optimistic Rollups, in which multiple off-chain transactions are aggregated into a single on-chain data representation and submitted to the main Ethereum chain.
Optimism utilizes a fraud-proof system, which assumes all aggregated rollup transactions are valid initially. Users can challenge these transactions and submit potential fraud proofs within a specified time frame. If any fraudulent activity is detected during this period, the malicious user is penalized, and the transaction is rolled back.
What Are the Use Cases of Base?
Like other L2 networks, Base can be used for a wide range of use cases. Here are some applications that have been built on Base.
1. Payment apps
Beam is a payment app that enables users to conduct transactions using either the stablecoin USDC or the app's native token, Eco. Users can sign in using their Twitter accounts and cover gas expenses through USDC or Eco. Additionally, Beam includes an integrated fiat-to-crypto and crypto-to-fiat conversion gateway.
2. Token swaps
Token swapping on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) allows users on Base to trade various cryptocurrencies. Currently there are several decentralized exchanges that are running on Base, such as Uniswap, Maverick and Dackieswap.
3. Liquidity provision
Users can provide liquidity on the Base blockchain through various DApps such as Uniswap, BaseSwap and Dackieswap. These DApps allow liquidity providers to earn fees from transactions in liquidity pools.
4. Bridging
Base has developed an official bridge known as the Base Bridge that is compatible with the majority of Ethereum wallets, such as MetaMask or Coinbase Wallet. Users are able to bridge ERC-20 tokens across Base and Ethereum.
Bridging from Ethereum to Base usually takes a couple of minutes, whilst bridging from Base to Ethereum takes roughly 7 days.
5. Launching DAOs
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs) is a blockchain based organization characterized by community driven decisions and operated through smart contracts. Aragon, a protocol for creating DAOs, has introduced a no-code DApp on the Base network, simplifying the DAO creation process.
Will There Be a BASE Token?
Base’s roadmap and official twitter bio state that they have no plans to issue a network token in the future.
However, projects may initially claim to have no plans for airdrops and execute an unannounced airdrop in the future. This is usually done to reward early supporters for contributing to the network and fostering a community.
How to Connect to the Base Network and Use the Testnet?
Connecting to the Base network is fairly straightforward, and it can be done with the Coinbase wallet or any EVM compatible wallet.
1. Connect to Base with a Coinbase wallet
To utilize Base with Coinbase Wallet follow the subsequent steps:
1. Launch the Coinbase Wallet browser extension and sign in to your account.
2. Connect to an application using Coinbase Wallet (in this example we will use BaseSwap).

3. Access the network selection menu by clicking the network symbol located in the top right corner.
4. Choose Base from the list.
5. The active network will now be set to Base.
2. Connect to Base with MetaMask
Users can connect to Base with numerous EVM wallets. Let’s see how to connect the Base network with the MetaMask wallet as an example.
1. Launch the MetaMask browser extension.
2. Access the network selection dropdown menu by clicking the dropdown button situated at the top of the extension.
3. Select the add network button.
4. Select add a network manually.
5. In the “add a network manually” dialogue box, input the following details for the Base Goerli testnet and click save:
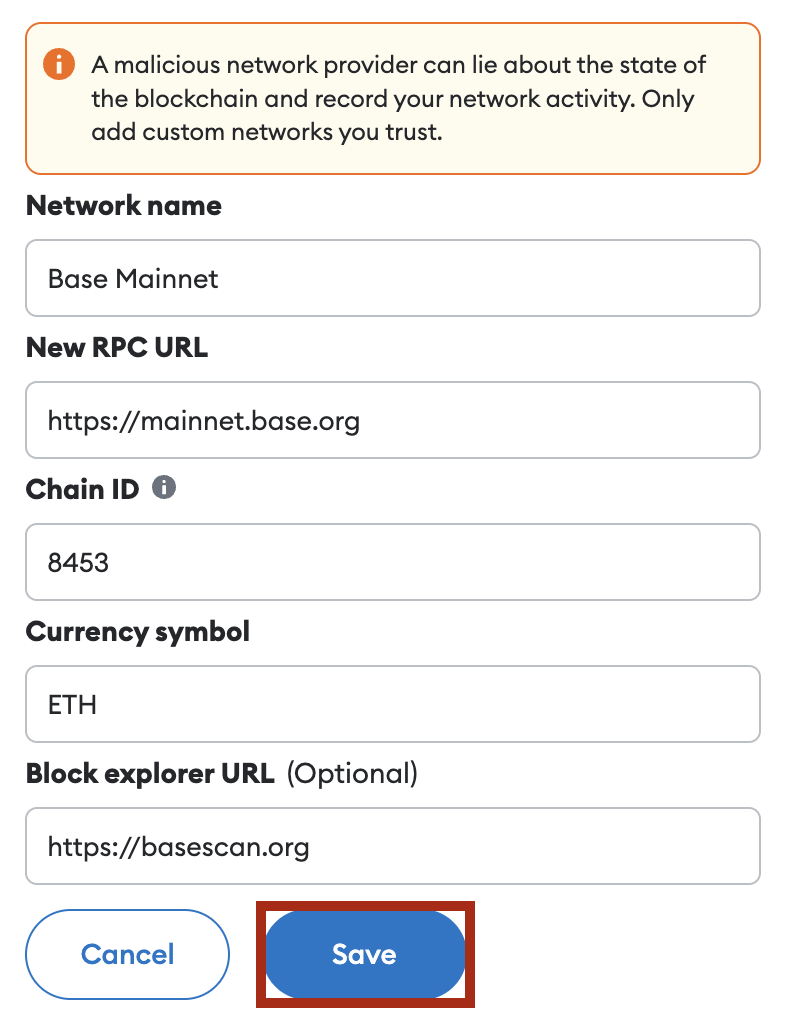
6. You should now be able to connect to the Base network in the network selection dropdown section.
What Are the Benefits of Base Network?
The key benefits of using the Base network include the following:
1. Low-cost
Like other optimistic rollups, Base features low gas fees, designed to significantly reduce transaction costs and enhance transaction throughput. It achieves this by processing transactions off-chain and consolidating them into a single proof.
2. Accessibility
EVM-compatible chains, like Base, improve accessibility by enabling developers to easily deploy and leverage existing Ethereum-based tools, frameworks, and smart contracts across multiple platforms.
3. Scalability
L2 scalability offers significant advantages by enhancing the capacity and transaction throughput of blockchain networks. This improvement addresses bottlenecks and reduces inefficiencies, ultimately providing quicker, more cost-effective solutions for users and developers.
What Are the Disadvantages of Base Network?
The primary limitations and concerns associated with Base are as follows:
1. Centralization
One of the primary concerns around Base is the degree of centralization. Coinbase functions as the only sequencer node on Base, giving them considerable control over transactions. A sequencer node is a specialized node in a blockchain network responsible for sequencing and finalizing transactions in a specified order, improving transaction throughput.
Having one sequencer node concentrates the power of transaction processing and ordering in a single entity. Additionally, this centralized authority has the ability to set and modify fees associated with the Coinbase Sequencer. Coinbase has hinted at the potential integration of third-party nodes in the future.
2. Long withdrawal periods
One of the main limitations of the Base blockchain is the long withdrawal periods, which takes approximately 7 days. This delay is attributed to the design of Optimism's fraud-proof system, which permits users to challenge transactions and submit potential fraud proofs within this specified time frame.
The long withdrawal periods could result in a suboptimal experience for users.
3. Security
As a L2 built on the OP Stack, Base faces a set of security risks. The first concern relates to the efficacy of fraud-proof mechanisms as a security measure.. Fraud proof relies on the vigilance of network participants to monitor and challenge any invalid off-chain transactions before they are finalized on the main blockchain.
However, this mechanism faces various challenges including reward incentive issues for participants and vulnerability to data withholding attacks.
Closing Thoughts
Base has gathered significant interest since its launch. It has hit a total of over one million users and over $385 million in total value locked (TVL) as of September 7, 2023. This incredible accomplishment places Base as the number 8 ranked chain in terms of TVL, overtaking popular blockchains such as Cardano and Solana.
As the first blockchain launched by a publicly traded company, Base is opening up new possibilities to attract a broader audience and bring more users into the world of Web3. As the platform continues to grow and evolve, it remains essential for users and developers to evaluate and make informed decisions when engaging with Base.
Reference: https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/what-is-base-coinbase-layer-2-network
